The 1st Junior Scientist Symposium will take place on April 25th from 16:00 to 17:00 (Swiss time)
Registration is now open!
Speakers:
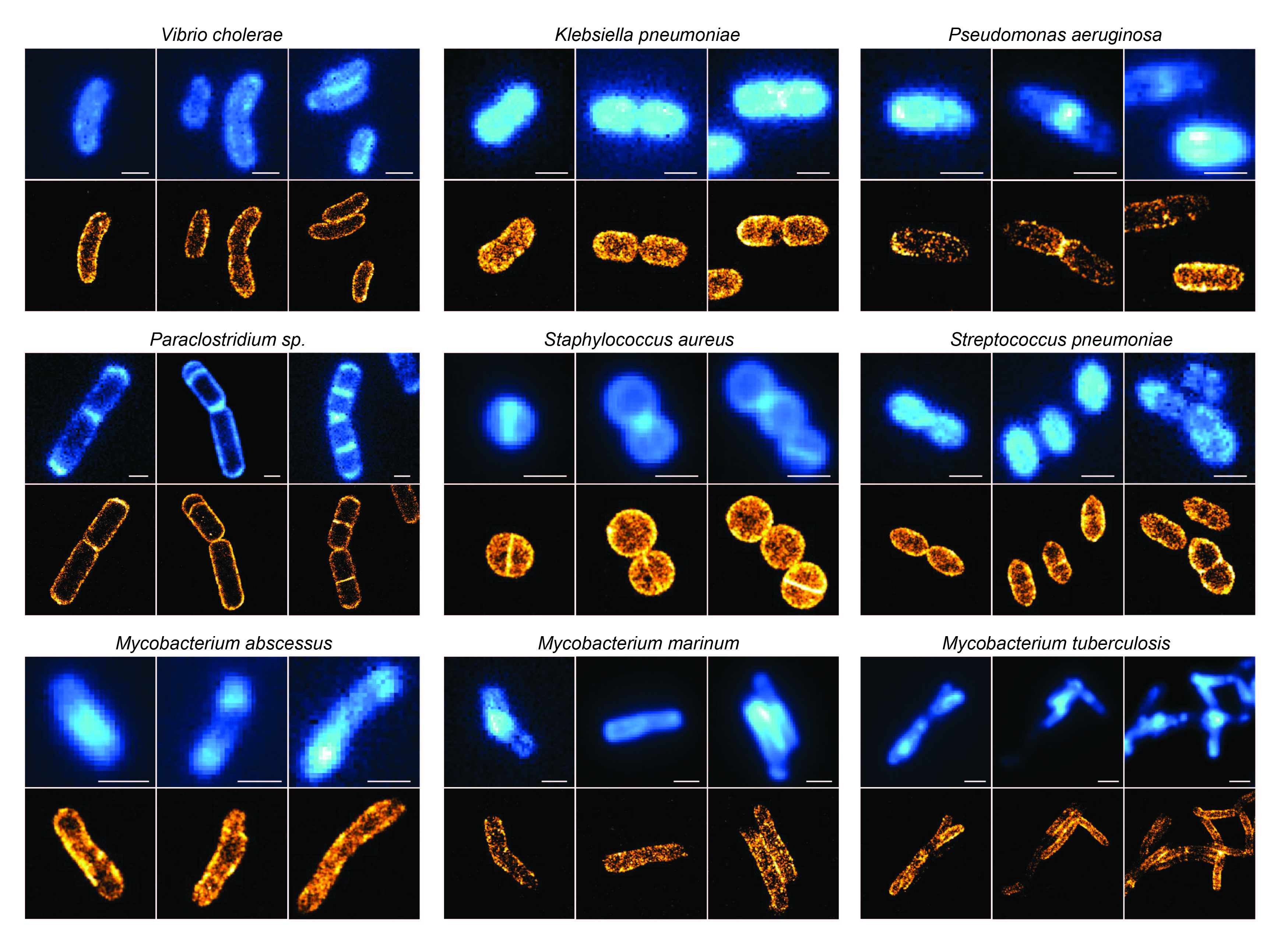
- Chen Zhang (Laboratory of Experimental Biophysics, EPFL)
Title: Fluorescent D-amino acids for STORM of the bacterial cell wall
Abstract: Fluorescent D-amino acids (FDAAs) have previously been developed to enable in situ highlighting of where bacterial cell wall growth occurs. Most bacterial cells lie at the edge of the diffraction limit of visible light; thus, resolving the precise details of peptidoglycan (PG) biosynthesis requires super-resolution microscopy after probe incorporation. Although super-resolution microscopy has been applied in a few cases to visualize FDAAs, stochastic optical reconstruction microscopy (STORM) has stringent requirements on the fluorophore photophysical properties, and therefore has remained challenging in this context. Here, we report the synthesis and characterization of new FDAAs compatible with STORM imaging. We demonstrate the incorporation of our probes, and their utility for visualizing PG at the nanoscale in gram-negative, gram-positive, and mycobacteria species. This improved FDAA toolkit will further endow researchers with a nanoscale perspective on the spatial distribution of PG biosynthesis.
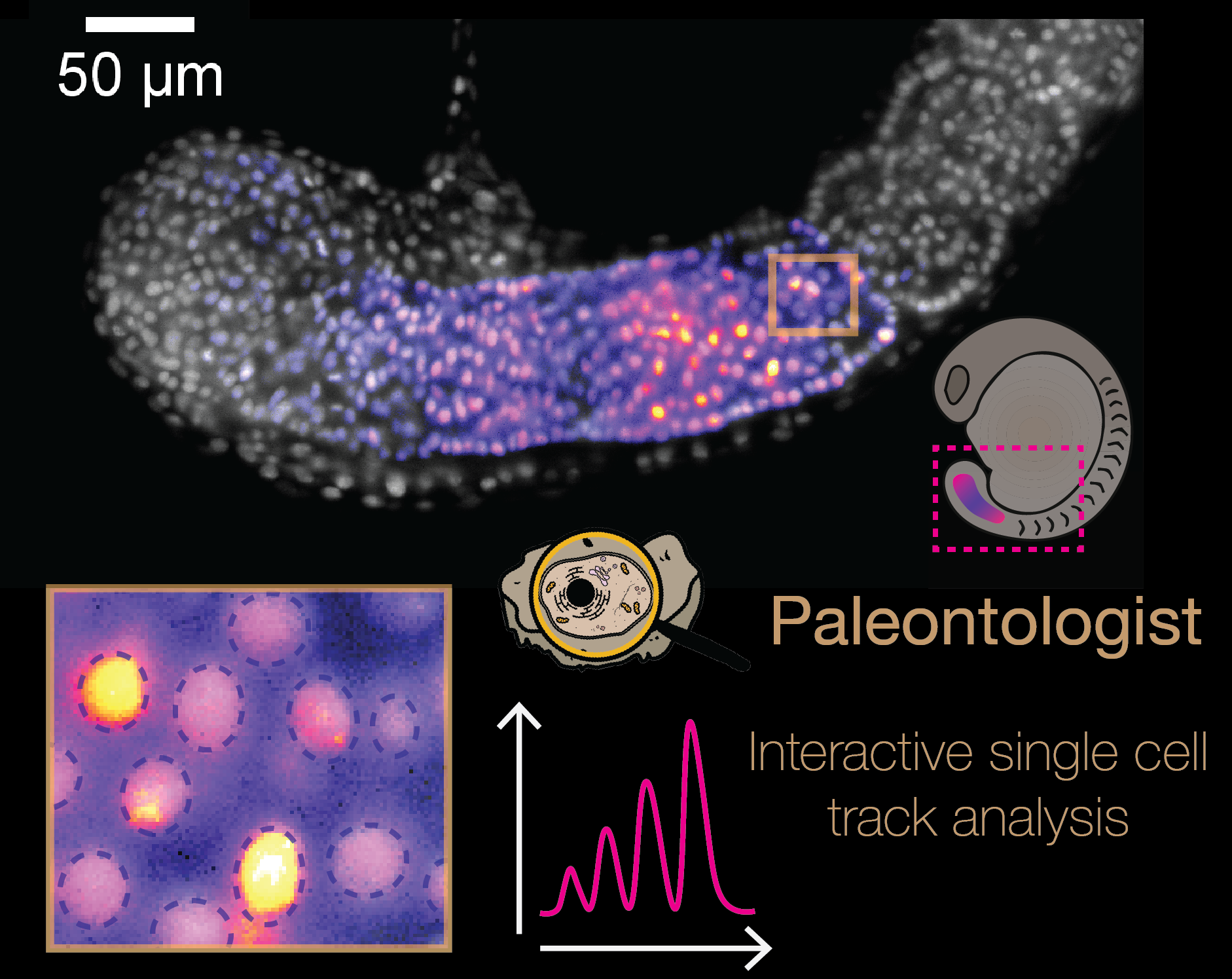
- Arianne Bercowsky Rama (Andrew Oates Group, EPFL)
Title: But, what are the cells doing? Image analysis pipeline to follow single cells in Zebrafish embryo
Abstract: Somitogenesis is a dynamic process during early embryonic development. This process gives rise to the backbone, ribs and associated muscles of the adult, and defects during developmental can result in congenital scoliosis. The rhythmicity of somite formation is controlled by the segmentation clock, a multi-cellular population of molecular oscillators. Advances in microscopy and live reporters allow us to visualise the segmentation clock’s travelling wave pattern across the segmenting tissue in the embryo. This wave pattern arises from the slowing down of cellular oscillations along the anteroposterior axis of the pre-segmental mesoderm (PSM). Because of the rapid oscillatory dynamics and imaging limitations, it has been historically difficult to quantify these dynamics at cellular-resolution during somitogenesis. Here we have developed an image analysis pipeline to quantitatively describe segmentation clock dynamics in cells within the embryo throughout somitogenesis. We use these imaging tools to investigate how precision in the tissue-level segmentation clock pattern and somite formation is created from underlying noisy dynamics in PSM cells.
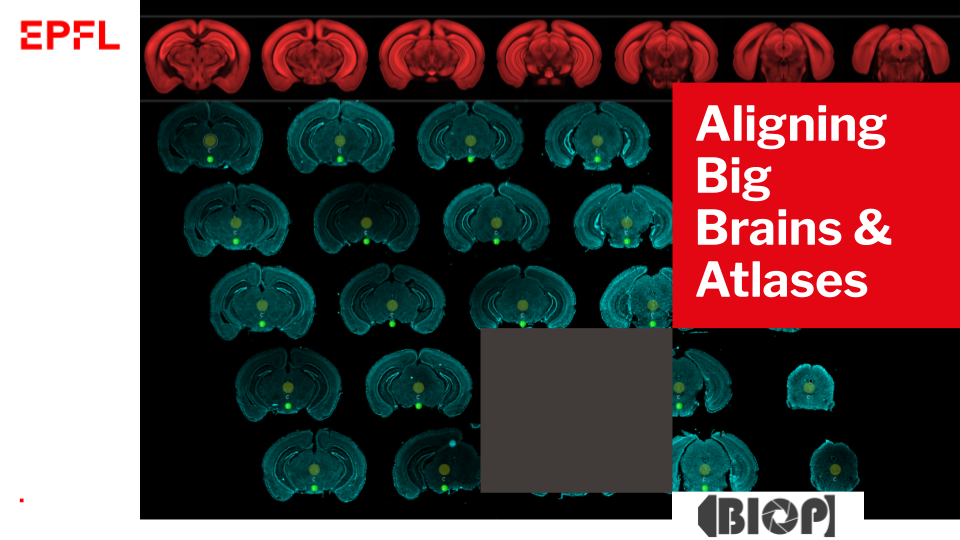
- Nicolas Chiaruttini (Bioimaging and Optics Core Facility, EPFL)
Title: Aligning Big Brains & Atlases: brain serial sections registration made easy with Fiji and QuPath
Abstract: Mapping image data to the allen brain atlas is a very common, important and often time-consuming and non-trivial task in neurological research. Open source and proprietary software tools have been developed to tackle this challenge with the disadvantages of being far from a one-size-fits-all solution.
Each software is typically tailored for a specific use case (3D vs 3D or 2D vs 3D registration, automated/manual, affine or free-form transformation). With Aligning Big Brains & Atlases (ABBA), we offer a unique combination of features in the current software landscape for 2D to 3D registration: support of multiresolution images in their native file format, a convenient user interface for positioning slices along the atlas and asynchronous computation of (potentially nonlinear) registrations. This is realized by using the abstract imglib2 image library and the bigdataviewer ecosystem of Fiji, which readily provides atlas reslicing in arbitrary orientations and on-the-fly computing of image transformations.
It takes 30 minutes for a trained user to perform a fully non-linear registration of 80 sections, including manual curation, on a ‘standard’ computer. The software contains modules to facilitate the communication with QuPath, which can be used for defining the initial data set, and for further downstream analysis after registration. The automated registration backend uses the elastix library, and manual edition of registration uses Fiji’s BigWarp plugin. It is moreover possible to control and extend ABBA's functionality with python programming language.